Working principle of Oil Pump
Working principle of Oil Pump

Bablu Yadav
Posted in Automobile Engineering
.
The lubricating oil pump is an integral part of the internal combustion engine which sucks the oil up from the oil sump and sends to the engine lubricating parts under a required pressure. Oil pump supply engine oil to various moving parts within the engine including pistons, crankshafts, camshafts and bearings. The lubrication prevents direct metal-to-metal contact, reducing friction and wear between components.
Before knowing how oil pump works let's first discuss what are the components of oil pump.
Components of oil pump
- Oil pump
- Oil control valve
- Suction pipe
- Connecting pipe (cross over pressure pipe)
- Direct drive pipe (oil separator)
- Frame reinforcement
- Pressure pipe
- Oil strainer
- Reduction valve (safety valve)
- Oil cooler
- Cooling duct cover
- Connecting block
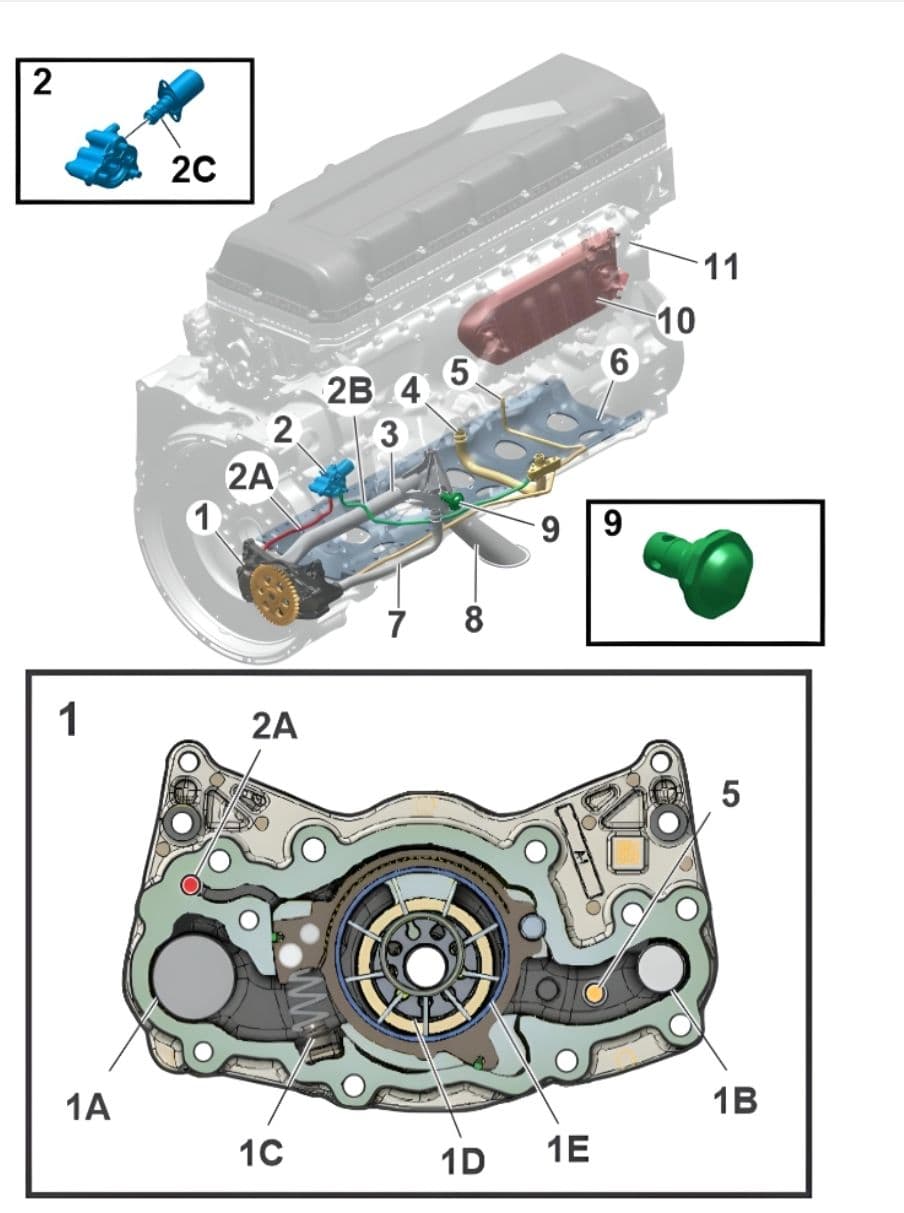
1A. Oil inlet from strainer
1B. Oil outlet from oil pump
1C. Spring
1D. Rotor
1E. Control ring
2A. Regulation port
2B. Supply pipe (oil control valve)
2C. Solenoid filter (oil control valve)
Working of Oil Pump
The oil pump (1) is a variable displacement pump located at the rear of the engine and mounted with four screws to the rear main bearing cap. The oil pump is driven by a gear directly from the crankshaft gear. The oil control valve (2) regulates the pressure flow to the engine based on the ECM (Engine Control Module) command. The oil control valve has a solenoid filter (oil control valve) (2C). The oil pump has a rotor (1D), a control ring (1E) and a spring (1C). The OCV opens and closes based on the main gallery pressure and the required pressure. Based on the closing or opening of the oil control valve, the pressure difference will counteract the spring (1C) and result in varying pressures developed inside the pump. The oil pump has a regulation port (2A). The oil control valve receives the filtered oil through the supply pipe (oil control valve) (2B) and is connected to the connecting block (12).
The oil pressure is regulated with the help of the pressure feedback to the oil pump and the oil pressure is regulated based on the engine requirements calculated by the ECM. The oil temperature, the engine torque requirement and the engine speed are the main inputs to the ECM for the actuation of the oil control valve.
When the solenoid filter (oil control valve) (2C) in the oil control valve is clogged, the complete oil control valve must be replaced. Refer to the spare parts information.
The oil is supplied directly from the outlet of the oil pump to the crankcase ventilation through the direct drive pipe (oil separator) (5). The reduction valve (safety valve) (9) protects the oil pump, the filter and the cooler against excess pressure when the oil viscosity is too high.
The suction system is in two parts and has a suction pipe (3) and an oil strainer (8). The plastic strainer is screwed to the stiffening frame. The metal pipe is sealed at the ends with rubber seals and is available in two lengths, depending on the oil pan used and how it is fitted. The pressure pipe (7) is made of steel and is attached to the cylinder block. A connecting pipe (cross-over pressure pipe) (4) is attached below the reinforcement frame, connecting the oil filter housing and the main gallery with the help of vertically drilled channels in the cylinder block.
The oil cooler (10) is screwed directly onto the cooling duct cover (11).