ENGINE Components
What are the main components of the Engine

Bablu Yadav
Posted in Automobile Engineering
.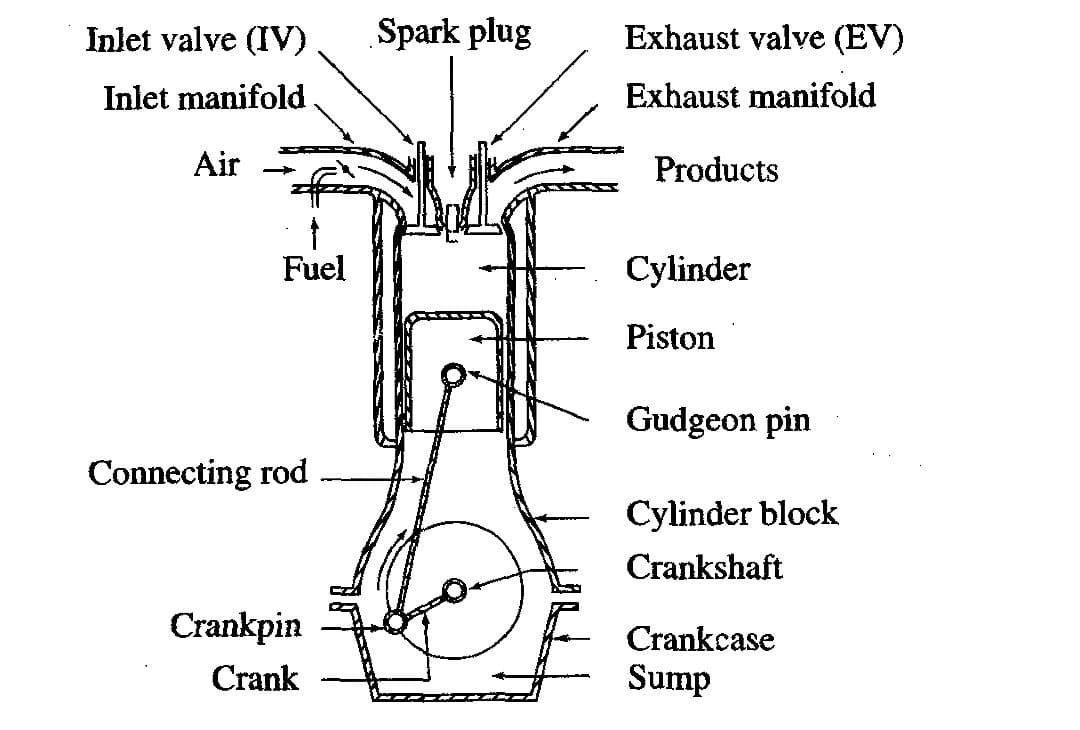
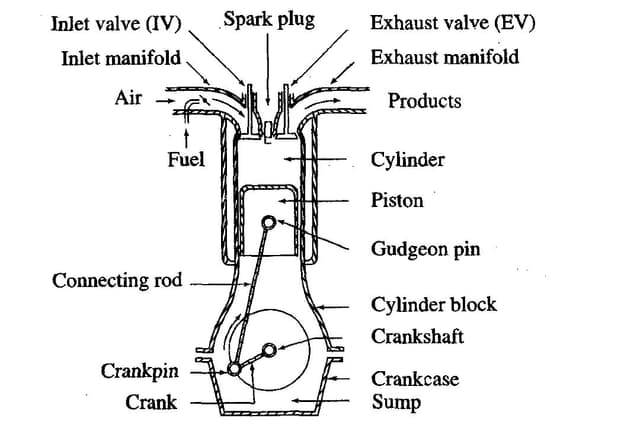
a) Cylinder block– The cylinder block is the main supporting structure for the various components. The cylinder of a multi cylinder engine are cast as a single unit, called cylinder block. The Cylinder head is mounted on the cylinder block. The cylinder head and cylinder block are provided with water jackets in the case of water cooling or with cooling fins in the case of air cooling.
b) Cylinder– As the name implies it is a cylindrical vessel or space in which the piston makes reciprocating motion. The varying volume created in the cylinder during the operation of the engine is filled with the working fluid and subjected to different thermodynamic processes. The cylinder is supported in the cylinder block.
c) Piston– It is a cylindrical component fitted into the cylinder forming the moving boundary of the combustion system. It fits perfectly (snugly) into the cylinder providing a gas-tight space with the piston rings and the lubricant. It forms the first link in transmitting the gas forces to the output shaft.
d) Combustion chamber– The space enclosed in the upper part of the cylin•der, by the cylinder head and the piston top during the combustion process, is called the combustion chamber. The Combustion of fuel and the consequent release of thermal energy results in the building up of pressure in this part of the cylinder.
e) Inlet manifold– The pipe which connect the intake system to the inlet valve of the engine and through which air or air-fuel mixture is drawn into the cylinder is called the inlet manifold.
f) Exhaust manifold– The pipe which connects the exhaust system to the exhaust valve of the engine and through which the products of combustion escape into the atmosphere is called the exhaust manifold.
g) Inlet and Exhaust valves– Valves are commonly mushroom shaped pop•pet type. They are provided either on the cylinder head or on the side of the cylinder for regulating the charge coming into the cylinder (inlet valve) and for discharging the products of combustion (exhaust valve) from the cylinder.
h) Spark Plug– It is a component to initiate the combustion process in Spark- Ignition (SI) engines andis usually located on the cylinder head.
i) Connecting Rod– It interconnects the piston and the crankshaft and trans•mits the gas forces from the piston to the crankshaft. The two ends of the connecting rod are called as small end and the big end (Fig.1.3). Small end is connected to the piston by gudgeon pin and the big end is connected to the crankshaft by crankpin.
j) Crankshaft– It converts the reciprocating motion of the piston into useful rotary motion of the output shaft. In the crankshaft of a single cylinder engine there are a pair of crank arm and balance weights. The balance weights are provided for static and dynamic balancing of the rotating system. The crankshaft is enclosed in a crankcase.
k) Piston rings– Piston rings, fitted into the slots around the piston, provide a tight seal between the piston and the cylinder wall thus preventing leakage of combustion gases.
l) Gudgeon pin– It links the small end of the connecting rod and the piston.
m) Camshaft– The camshaft (not shown in the figure) and its associated parts control the opening and closing of the two valves. The associated parts are push rods, rocker arms, valve springs and tappets. This shaft also provides the drive to the ignition system. The Camshaft is driven by the crankshaft through timing gears.
n) Cams– These are made as integral parts of the camshaft and are so designed to open the valve at the correct timing and to keep them open for the necessary duration.
o) Flywheel– The net torque imparted to the crankshaft during one complete cycle of operation of the engine fluctuates causing a change in the angular velocity of the shaft. In order to achieve a uniform torque an inertia mass in the form of a wheel is attached to the output shaft and this wheel is called the flywheel.
p) Carburetor– Carburetor is used in petrol engine for proper mixing of air and petrol.
q) Fuel pump– Fuel pump is used in diesel engine for increasing pressure and controlling the quantity of fuel supplied to the injector.
r) Fuel injector– Fuel injector is used to inject diesel fuel in the form of fine atomized spray under pressure at the end of compression stroke.1.2.2
What are The Terminologies used in IC engine–
A cross section of a single cylinder spark-ignition engine with overhead valves is shown in Fig. The major components of the engine and their functions are briefly described below.
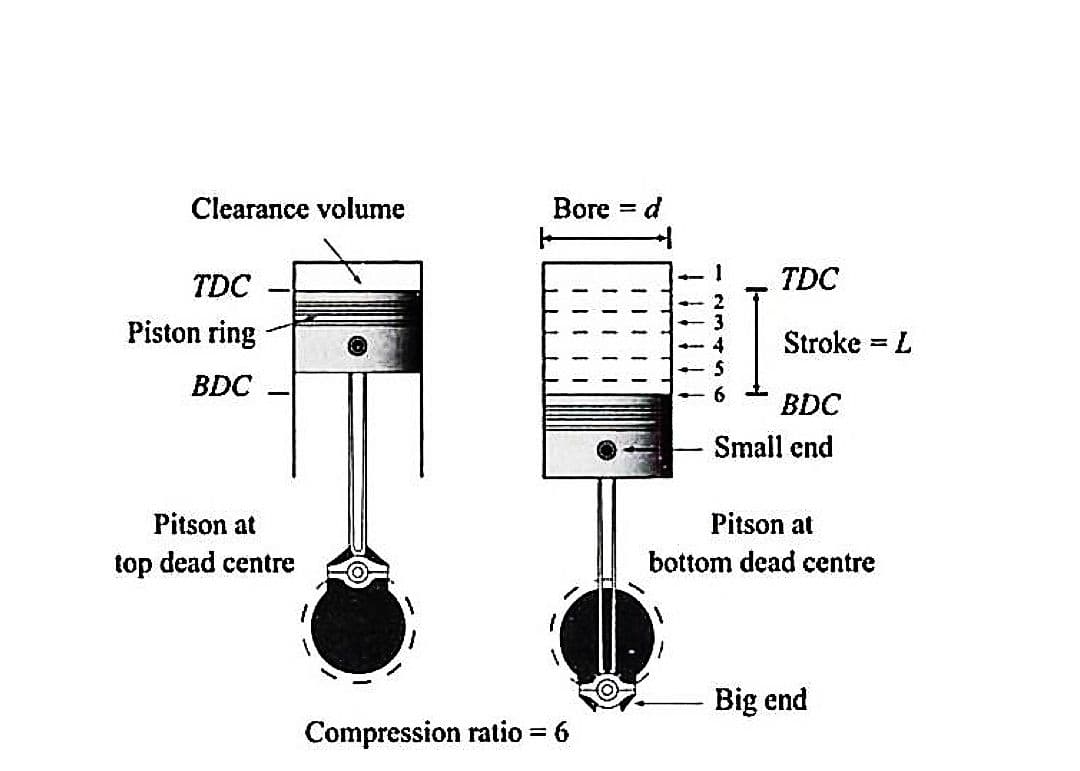
◾Cylinder Bore (d): The nominal inner diameter of the working cylinder is called the cylinder bore and is designated by the letter d and is usually expressed in millimeter(mm).
◾Piston Area (A): The area of a circle of diameter equal to the cylinder bore is called the piston area and is designated by the letter A and is usually expressed in square centimetre (cm2).
◾Stroke (L): It is the linear distance traveled by the piston when it moves from one end of the cylinder to the other end. It is equal to twice the radius of the crank. Itis designated by the letter L and is expressed usually in millimeter (mm).
◾Stroke to Bore Ratio (L/d): L / d ratio is an important parameter in classifying the sizeof the engine.– If d < L, it is called under-square engine.– If d = L, it is called square engine.– If d > L, it is called over-square engine. An over-square engine can operate at higher speeds because of larger bore and shorter stroke.
◾Dead Centre:In the vertical engines, top most position of the piston is called Top Dead Centre (TDC).When the piston is at bottom most position, it is called Bottom Dead Centre (BDC).In horizontal engine, the extreme position of the piston near to cylinder head is Called Inner Dead Centre (IDC.) and the extreme position of the piston near the crank is Called Outer Dead Centre (O.D.C.).
◾Displacement or Swept Volume (Vs): The volume displaced by the piston in one stroke is known as stroke volume or swept volume. It is expressed in terms of cubic centimetre (cc) and given by
𝑉𝑠 = 𝐴 × 𝐿 =𝜋𝑑2𝐿4
◾Cubic Capacity(CC) or Engine Capacity: The displacement volume of a cylinder multiplied number of cylinders in an engine will give the cubic capacity or the engine capacity.For example, if there are K cylinders in an engine, The Cubic capacity =Vs × K
◾ Clearance Volume (Vc): It is the volume contained between the piston top and cylinder head when the piston is at top or inner dead center.
◾ Compression Ratio (r): The ratio of total cylinder volume to clearance volume is called the compression ratio (r) of the engine.
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑐𝑦𝑙𝑖𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑟 𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒
r= ————————————————————
𝐶𝑙𝑒𝑎𝑟𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒 𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒
∴ 𝑟 =𝑉𝑐 + 𝑉𝑠𝑉𝑐
For petrol engine r varies from 6 to 10 and for Diesel engine r varies from 14 to 20.
◾Piston speed (Vp): It is average speed of piston. It is equal to 2LN, where N is speed of crank shaft in rev/sec.
2𝐿N
Vp= ——————————
60𝑚⁄𝑠𝑒𝑐
where, L = Stroke length,
N = Speed of crank shaft,