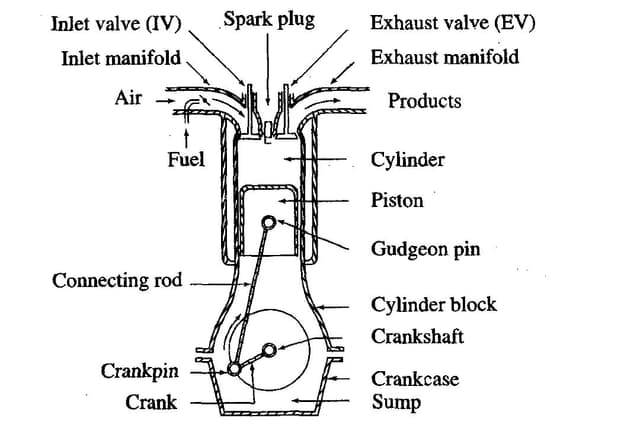
What is Regeneration of DPF
Regeneration of DPF

Bablu Yadav
Posted in Automobile Engineering
.
Regeneration
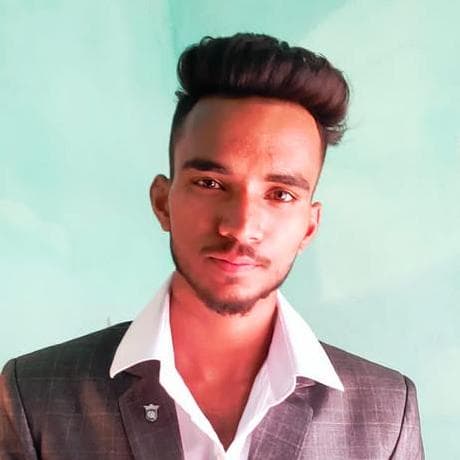
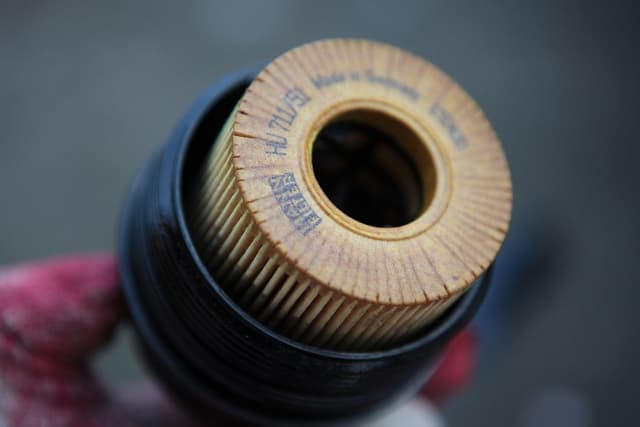
Under normal operating conditions, by-products from the engine combustion are collected in the aftertreatment system (soot and carbon in the DPF and sulphur in the SCR) unit. The process in which the particles of soot and sulphur are oxidised is called regeneration. Over time these by-products build up in the system, which increases the back pressure and increasingly impairs the aftertreatment system ability to clean the exhaust. This increases wear on the engine and the risk of damaging the engine and the aftertreatment system.
How to prevent the risk of damaging the engine and the aftertreatment system
To prevent this risk, remove soot and carbon regularly from the DPF and sulphur from the SCR converter. The particles of soot and sulphur are oxidised through regeneration, which increases the exhaust temperature. The ECM calculates levels and driving conditions and when a specific level is reached, it initiates regeneration. Regeneration can take place in the following ways:
Passive regeneration of DPF
Active soot regeneration of DPF
Active sulphur regeneration of SCR unit
Parked by driver
In workshop using diagnostic tool
Does fuel affect the Regeneration Sulphur in the fuel inhibits regeneration, so a low sulphur content in the fuel (EN590 or equivalent) is important for effective exhaust aftertreatment.
The ash that collects in the DPF cannot be oxidised away through regeneration, so the DPF must be cleaned manually at a service workshop according to the service schedule.