Coolant Pump
What is coolant pump and how it works

Bablu Yadav
Posted in Automobile Engineering
.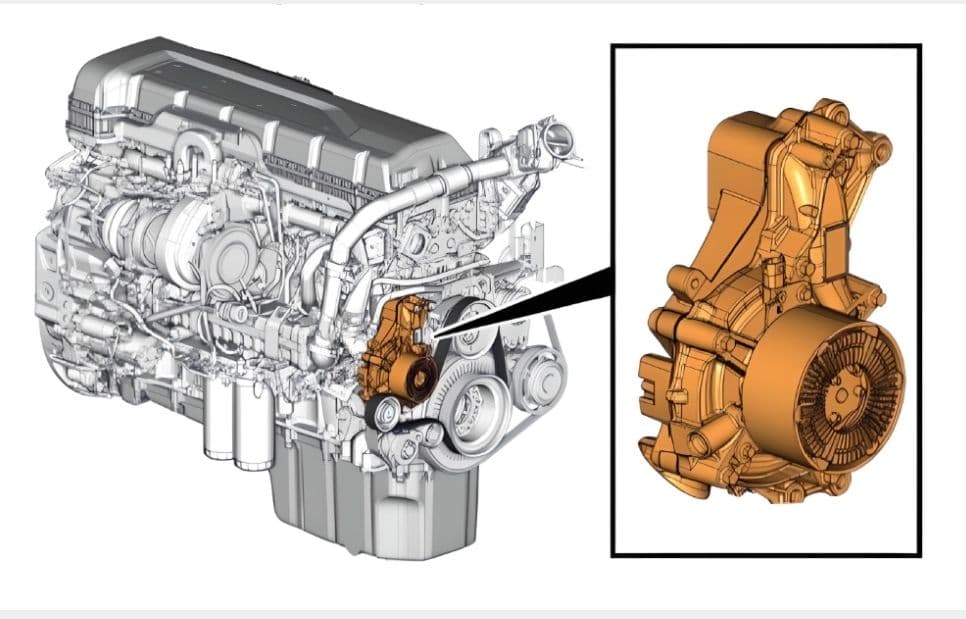
Coolant Pump
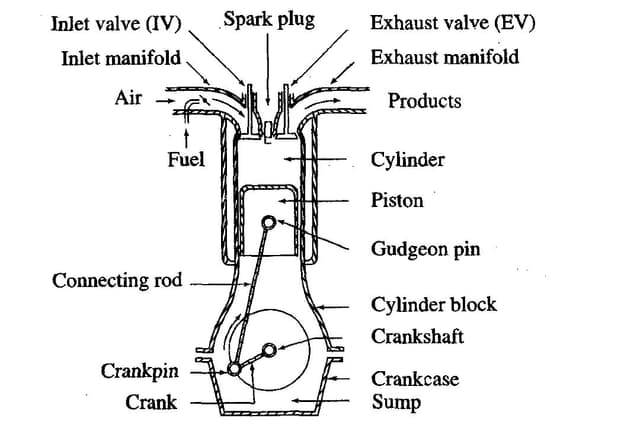
The coolant pump is a centrifugal type with electromagnetic coupling and is belt driven. This electromagnetic coupling enables the coolant pump to run at two speeds: a normal speed when the engine requires more cooling and a lower speed when the engine requires less cooling.
Working of Coolant Pump
The coolant pump is controlled by the ECM (Engine Control Module). The coolant pump casing is made of aluminium. At normal speeds, the electromagnetic coupling is activated (battery powered) and the impeller inside the coolant pump rotates at the same speed as the pulley on the outside. When the cooling requirement is reduced, the electromagnetic coupling is deactivated (voltage supply is zero), and a magnetic slip function reduces the speed of the impeller in relation to the pulley. Since the slip coupling function is magnetic, components in the coupling do not wear. The coolant pump is available with two different sizes of pulley.
▪️A smaller Puli which gives a higher output for vehicles with a retarder that requires more cooling.
▪️A larger Pulley verb vehicles without a retarder
There are channels on the rear side of the coolant pump for distributing the coolant, and the front houses a plastic impeller, shaft seal, bearing and pulley with electromagnetic coupling. The shaft bearing is a permanently lubricated combined roller bearing.
How coolant pump is lubricated
The seal between the impeller and bearing in the coolant pump is lubricated by coolant which is very less amount passes through the seal. Due to this, dried coolant residue will get accumulated around the drain hole. The accumulation of coolant residue is normal and does not indicate that the coolant pump need to be replaced.