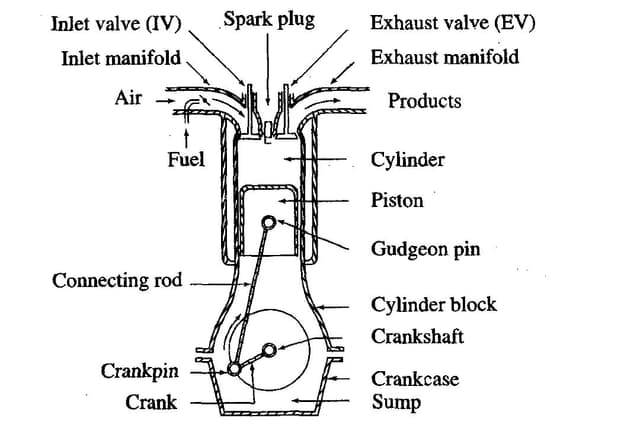
BIODIESEL
BIODIESEL

Bablu Yadav
Posted in Automobile Engineering
.
Biodiesel is a product made from renewable resources such as vegetable oils or animal fat.
The fuel is produced by the process called transesterification—in which the fats and oils gets converted into biodiesel and glycerin (a coproduct).
Biodiesel
Biodiesel that has been chemically processed into fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) can be blended with distillate diesel fuel and can be used in some diesel engines.
Rapeseed methyl ester (RME) is the most common type of FAME (fatty acid methyl ester) used in Europe. Soy methyl ester (SME) and sunflower oil methyl ester (SOME) are the most common types of FAME used in the US. Although use of FAME biodiesel is now a legal requirement in some markets, it is not as suitable for use in diesel engines as conventional diesel fuel or HVO (hydro-treated vegetable oil) are being used.
Effects of biodiesel on engine oil:
Using biodiesel can lead to increased oil dilution. Use engine oil analysis tools frequently to check for fuel dilution and monitor engine oil condition. Check the engine oil level daily. Always change the engine oil if the oil level rises above the maximum fill level.
Effects of biodiesel on fuel systems:
Biodiesel dissolves and loosens some fuel system deposits. During the initial conversion to biodiesel, loosened deposits will travel to the fuel filters and require more frequent fuel filter replacements. Start with new fuel filters when using biodiesel for the first time.
Biodiesel is aggressive to some materials used in fuel system components. Inspect seals, hoses, rubber and plastic components every 10 hours. Repair or replace any components that are damaged, softened or leaking. Clean biodiesel from painted surfaces immediately to prevent paint damage.
Biodiesel is more sensitive to bacteria and water contamination than distillate diesel fuel. Use as much fuel as possible before refilling the fuel tank in order to prevent bacteria growth if a machine is in regular use, e.g. regularly uses up a tank of fuel within a week. In climates where condensation is a risk, or when the machine is working for short durations, keep the fuel tank full.
Do not use biodiesel in machines with low utilization or operating time. Do not rest the machines for more than 4 weeks without flushing biodiesel out of the fuel system by operating the machine through at least one full tank of distillate diesel fuel.
Effects of biodiesel on exhaust aftertreatment systems:
Biodiesel leaves higher levels of ash in diesel particulate filters and may require more frequent diesel particulate filter (DPF) regeneration and cleaning, Biodiesel can cause deviations in temperatures and functionality of the DPF burner and may cause fault codes or errors.
Biodiesel exhaust gas is aggressive to some materials used in selective catalytic reduction systems (SCR) and may require more frequent cleaning, repairing or replacing of SCR parts.
Effects of biodiesel on cold weather:
Operation Biodiesel has a high viscosity at temperatures below 0°C (32°F) and may cause problems starting the engine. Use a fuel heater or park machines in a heated building if possible.
Effects of biodiesel on engine performance:
Biodiesel B100 has about 8% lower energy density compared to regular diesel fuel. Blends equal or lower than B20 have a small impact on engine performance.
Conclusion:
Biodiesel is not too good for any vehicle or machine as it has bad effects on ;
- Engine Performance
- Engine fuel system
- Exhaust After treatment process
- Cold weather
Always follow the manufacturer's storage recommendations and "best-before" dates for each delivery of biodiesel.