Engine oil
Engine oil

Bablu Yadav
Posted in Automobile Engineering
.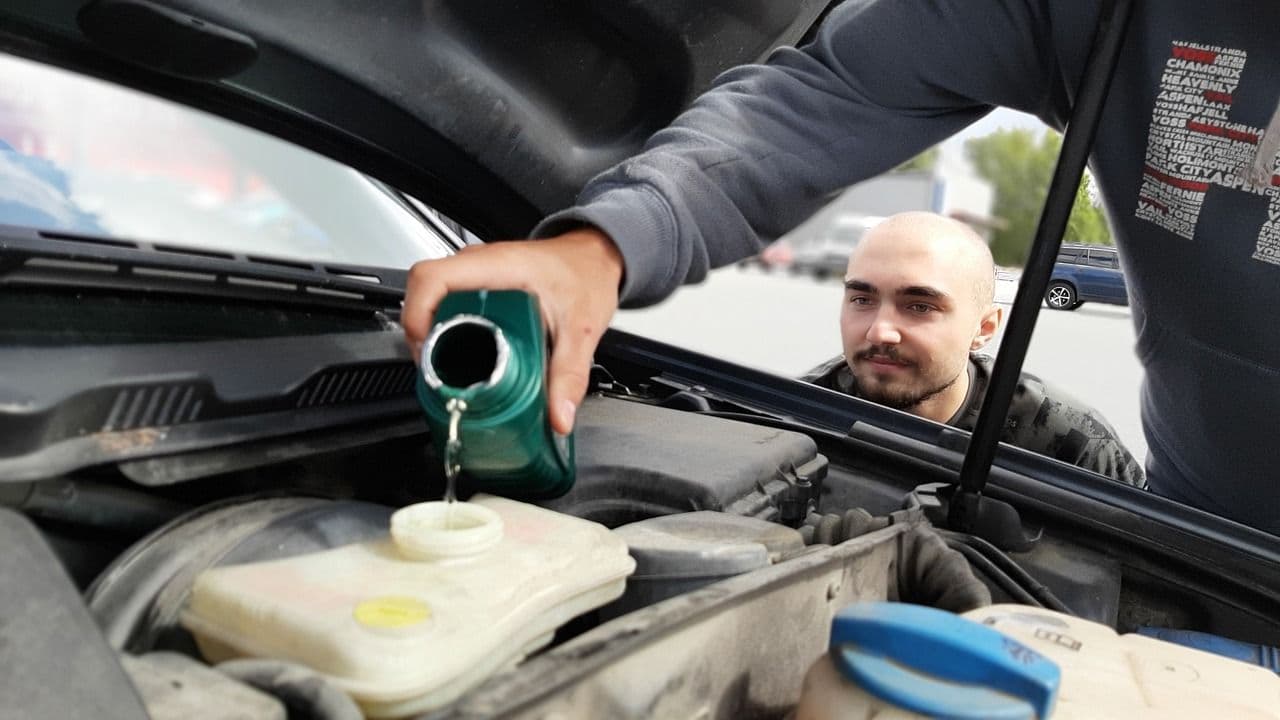
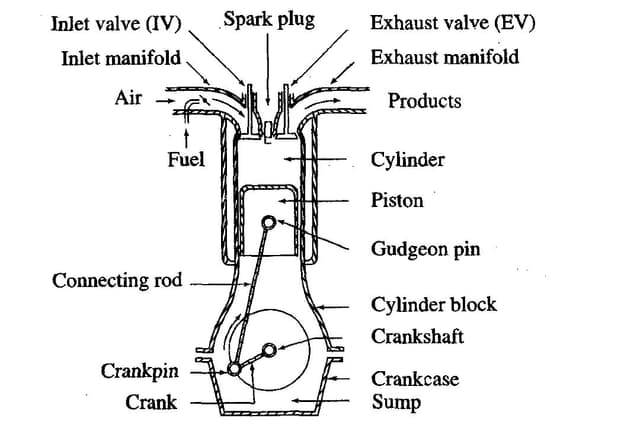
The main function of an engine oil is to reduce friction and thereby minimise wear between the moving parts of the engine. The oil should also absorb heat from parts that are exposed to extreme heat loads, and keep the engine components free from impurities by transporting these to the filter, from where they can be removed from the engine. Engine oil should also help in sealing between the cylinder wall and the piston.
Hazards
Engine oil must be treated as a hazardous material. The instructions for introduction and use of such materials must be strictly adhered too.
Formulation
An engine oil consists of a base oil and additives, where the base oil is either a mineral oil or a synthetic oil. The additives comprise a DI (Detergent Inhibitor) packet, a viscosity modifier (VM), and so-called pour point depressant (PPD). The DI packet comprises a combination of many components, of which the most Important are: Anti-wear agent
Anti-wear agent is normally based on Zinc-Dialkyl-Dithio Phosphate (ZDDP), which creates a protective, lubricating film on metal surfaces at high temperatures and at high pressure. A modern engine oil normally contains 0.1-0.15% zinc (Zn) and phosphor (P).
Detergents
Detergents help to keep the engine clean from coatings, for example in the piston ring grooves, and neutralize acidic combustion products, that otherwise attack and corrode metal parts such as cylinder liners and ball bearings. Detergents contain metals, normally Calcium (Ca) and/or Magnesium (Mg) in quantities of 0.2-0.5%.
Dispersants
Dispersants are additives that are often free from metals and are added to hold contaminants, mainly soot, suspended in the oil and thus avoid flocking, blockage of the lubricating system and abrasive wear.
Anti-oxidants
Anti-oxidants delay oxidation of the oil by counteracting reactions with by-products that are formed during incomplete combustion. The DI packet can even comprise other constituents, such as corrosion inhibitors, foam dampers and drip point retarders.
Viscosity modifiers
Viscosity modifiers are products with a high molecular weight (polymers) that combat viscosity reduction at high temperatures.