Chassis
This is the main machine portion having all the components required for the operation and running of the automobile.

Bablu Yadav
Posted in Automobile Engineering
.
Introduction:
This is the main machine portion having all the components required for the operation and running of the automobile. Therefore, the portion of the automobile without body is called chassis
The layout of chassis component :
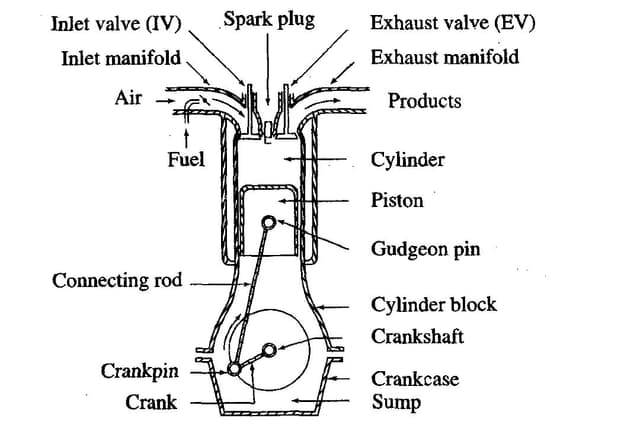
1. Power unit :
It consist of an internal combustion engine. It is mounted at the front of the vehicle. The clutch and gear box are placed behind it. These three components i.e., engine, clutch and gearbox are assembled into a single unit.
2.Propeller shaft :
For connecting the output shaft of the gear box to the differential, a long shaft called propeller shaft is used. It is fitted with universal joints to allow changes in the shaft alignment during rise and fall of the rear axle due to uneven road surface.
3.Rear axle :
It is a tube like shaft enclosing driving shaft for rotating wheels and enlarged at the center for enclosing the final drive gears. It is mainly used for Speed reduction, between the engine and the driving wheels.
4.Front axle :
It is used for mounting and steering front wheel carried on stub axle and swivelling upon King pins at the axle extremities.
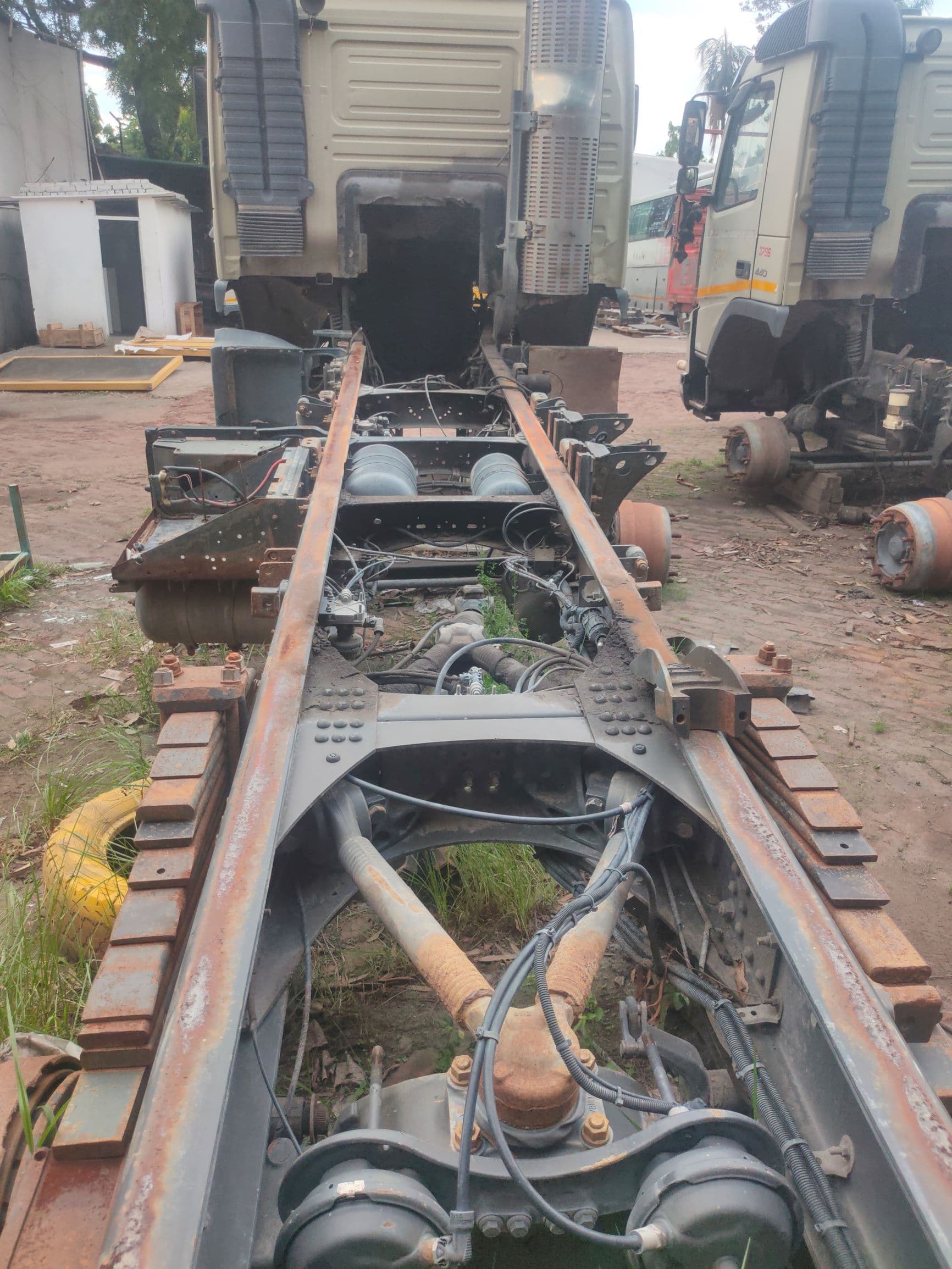
5.Frame :
It is a foundation for mounting engine and body of the vehicle as well as steering, power train and other chassis components. It may be made of box, tubular channel or U-shaped section welded or riveted together. To make them rigid, cross members are used. When the engine, wheels, power train and steering system are fitted on the frame, the assembly is known as chassis. The side members of the frame are tapered in the front for providing space for turning of the front wheels when steered . However, the rear side is curved upward to provide space for the rear springs and bouncing of the rear axle.
6.Brakes :
Controlling the movement of the vehicle, efficient brake system is necessary. The break components like brake pedal, master cylinder, wheel cylinders and break pipes are all mounted on the frame as per the chassis layout.
7.Electrical equipment :
Provision for electrical equipments is also made in the chassis layout. Indicator lights at front and rear during darkness, fog lights, side lights, headlights, stop lights, windscreen wiper and horn etc. require electricity for their operation. Their need is full filled by providing generator driven by the vehicle engine or buy a battery kept charged by the generator. The same battery helps to start the engine with starter motor attached to the engine and provides initial supply of the ignition system for petrol engine
The engine is located at the front of the vehicle. Followed by a clutch, gearbox, propeller shaft, universal joint, differential and back axle etc. The various other components of the vehicle of the layout are dynamo, horn, steering box, fan, fan pulley, crankshaft pulley, carburetor, air cleaner, ignition coil, distributor, gear control, steering wheel, brake pedal, clutch pedal and wheels etc. The power developed the engine is conveyed to the rear wheels through propeller shaft, universal joint, differential and half shafts systematically.
Types of chassis
1.Conventional Chassis
2.Non-Conventional Chassis
3.Full forward
4.Semi forward
5.Bus chassis
6.Engine in front
7.Engine at the center