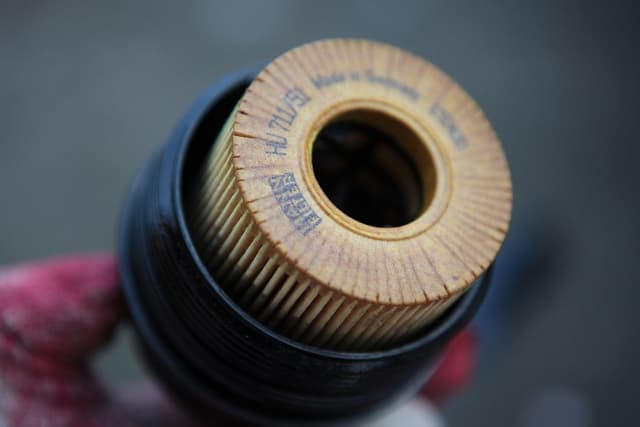
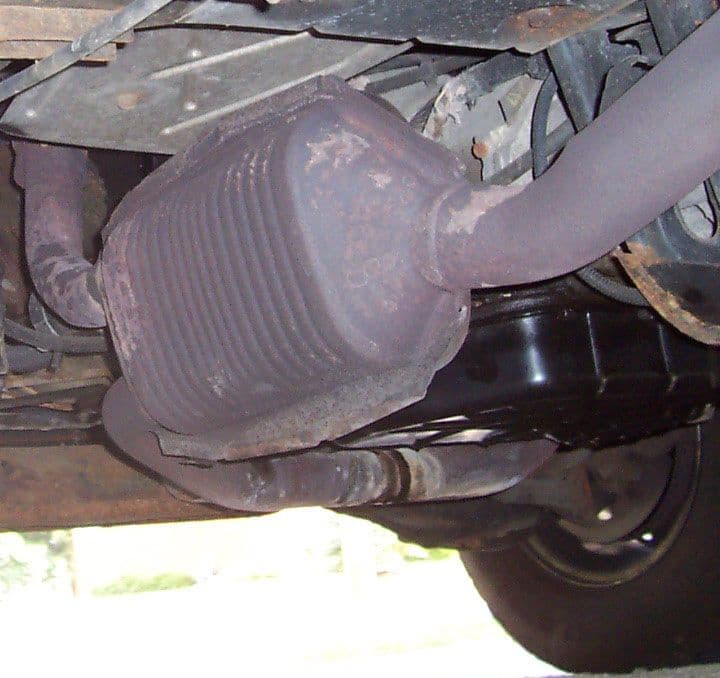
Catalytic Converter
A catalytic Converter is a cylinder like unit mounted in the exhaust system of the vehicle. In which the exhaust gases from the engine are passed through the converter, here the gaseous pollutants are converted into harmless gases.

Bablu Yadav
Posted in Automobile Engineering
.
What is a Catalytic Converter?
A catalytic Converter is a cylinder like unit mounted in the exhaust system of the vehicle. In which the exhaust gases from the engine are passed through the converter, here the gaseous pollutants are converted into harmless gases.
Where it is located and what it does?
It is placed between the exhaust manifold and the silencer of the vehicle.
If we look inside a catalytic converter, it has a honeycomb structure of a ceramic or metal coated with alumina base material and after that we get a second coating of precious metal like platinum or rhodium or combination of both are applied. The second coating serves a catalyst which is a substance that causes a chemical change without any reaction in the system. And thus, the toxic gases like Carbon monoxide (CO) , Hydrocarbon (HC) and Nitrogen oxide (NOx) are converted into harmless Carbon dioxide (CO2) , Hydrogen (H2) and Nitrogen (N2).
There are two types of catalytic converters :
(1) A two-way converter.
(2) A three-way converter.
(1) A two-way converter :
It is used to control only CO and HC emissions by oxidation. CO and HC in the exhaust gases unite with oxygen and form H2O and CO₂
(2) A three-way converter:
It is mostly used in all petrol vehicles especially in cars. It controls CO and HC by oxidation and NOx by reduction. The three way converter operates in two stages. The first stage of the converter uses radium to reduce the NOx (Nitrogen oxide) in the exhaust into nitrogen and oxygen. In the second stage of converter, platinum acts as oxidation catalyst to change HC and CO into harmless water and CO2. The oxygen required in the second stage is obtained from the air supplied to the exhaust after the first stage. The catalyst allows the oxidation of the exhaust gases at a much lower temperature than in the combustion chamber. When the temperature exceeds 300°C, the conversion efficiency of a new converter is about 98% for CO and about 95% for HC. The outgoing exhaust gases in a petrol engine are at a temperature of 300 to 400°C during idling of the engine and reaches about 900°C under full load conditions. The converters operate efficiently between 400°C and 800°C.
Things to remember :
Automobile fitted with catalyst converter should be run on unleaded gasoline because impurities in the fuel shorten the life of the catalyst. Therefore this lead free gasoline provides a service life from 80,000 to 100,000 km of the catalytic converter without any maintenance or servicing.
1.) Every care should be taken to avoid overheating of the converter due to over rich mixture, late timing or misfiring which can melt catalyst element.
2.) Too close of the catalyst converter to the exhaust manifold can cause to exceed the safe working temperature, thereby reducing the converter life.