Brake Booster
When it comes to ensuring vehicle safety, one of the necessary components that plays an important role in effective braking is the brake booster. This simple but important device is responsible for increasing the efficiency of the brake system.

Bablu Yadav
Posted in Automobile Engineering
.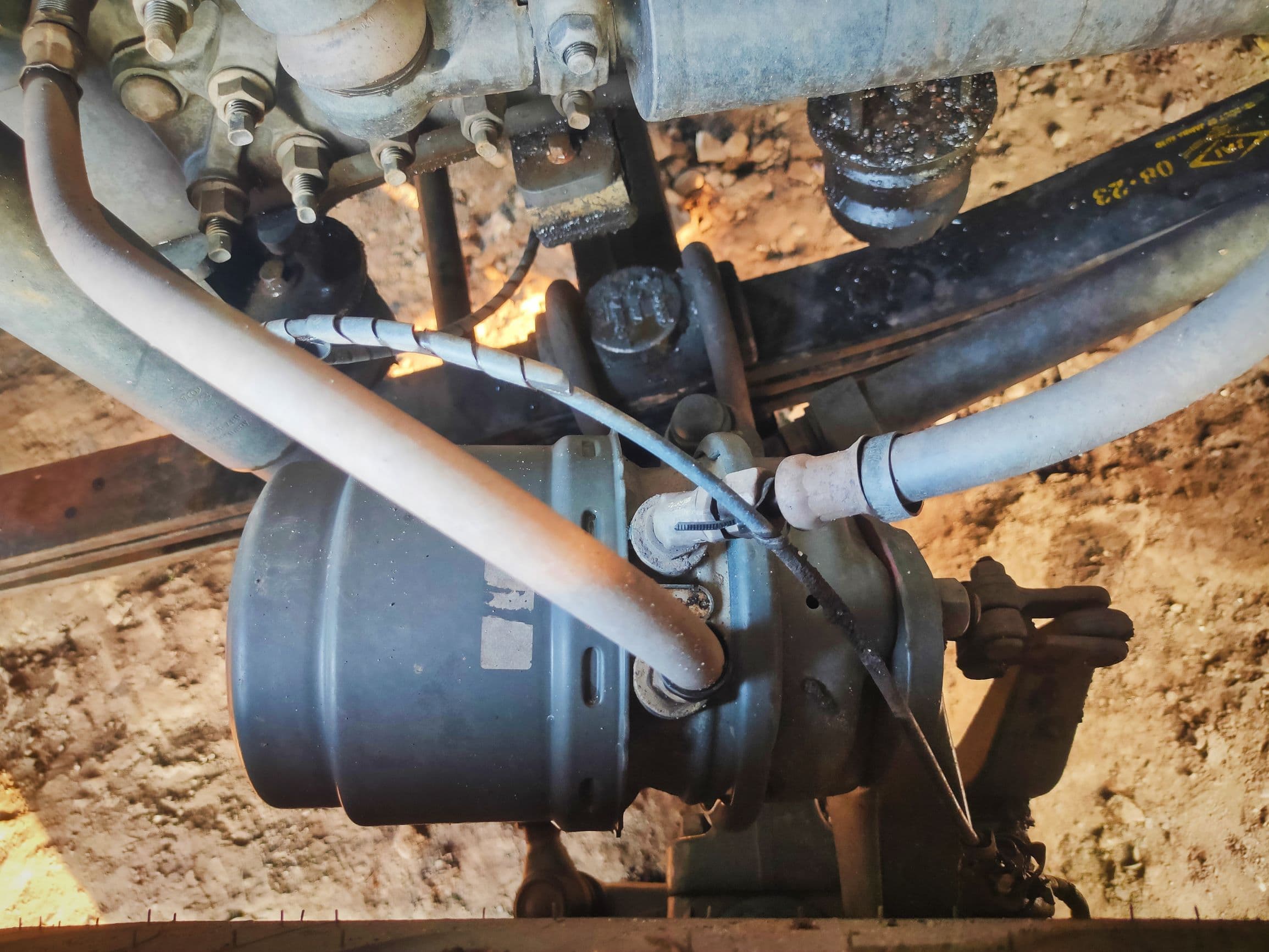
When it comes to ensuring vehicle safety, one of the necessary components that plays an important role in effective braking is the brake booster. This simple but important device is responsible for increasing the efficiency of the brake system. In this blog , we will understand it's components, operation, and essential functions.
The Brake Booster
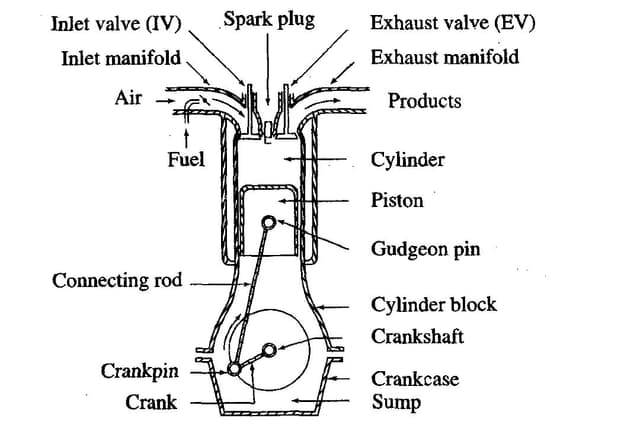
The brake booster, also known as a vacuum brake booster or power brake booster, is a device designed to assist the driver in applying the necessary force to the brake pedal. It operates on the principle of utilizing engine vacuum to make braking more efficient.
Components of a Brake Booster :
1. Housing:
The external casing of the brake booster, typically made of metal, enclosed by all the internal components. It connects with both the brake pedal and the master cylinder.
2. Diaphragm:
The diaphragm is the central element of the brake booster. It is a flexible rubber or rubber-like membrane that divides the booster's interior into two chambers: the vacuum side and the atmospheric side.
3. Vacuum Hose:
The vacuum hose also called break booster hose links the brake booster to the engine's intake manifold, providing the required vacuum pressure for the booster to operate.
4. Check Valve:
Often positioned within the vacuum hose, a check valve permits air to flow in only one direction. This ensures the maintenance of vacuum pressure, even when the engine is not running or in the case of a vacuum leak.
How a Brake Booster Operates
The operation of a brake booster is a coordinated process that combines mechanical and vacuum forces.
Here's how it works:
1. When the driver presses the brake pedal, it pushes on a rod that extends into the brake booster.
2. The diaphragm inside the brake booster is connected to this rod. As the brake pedal is pressed, it moves the diaphragm forward, creating a vacuum in the vacuum chamber.
3. Atmospheric pressure on the other side of the diaphragm pushes against it, assisting the driver in applying the brakes. This system reduces the amount of physical force the driver needs to apply on the brake pedal.
4. As the engine operates, it generates a vacuum in the intake manifold. The vacuum hose connected with the brake booster allows this vacuum to be applied to the booster. This vacuum amplifies the force applied by the driver, resulting in more efficient braking.
Functions of a Brake Booster:
1. Enhanced Braking Power:
The primary function of a brake booster is to assist the driver in applying the brakes with less effort. It multiplies the force applied to the brake pedal, making it easier to stop the vehicle effectively.
2. Improved Safety:
By reducing the physical effort required for braking, brake boosters contribute significantly to safety. Drivers can maintain better control of the vehicle, especially in emergency braking situations.
3. Consistent Brake Feel:
Brake boosters helps in ensuring a consistent and predictable feel to the brake pedal in both cases either the engine is idling or running. This consistency is much important for safe and reliable braking.
Conclusion
The brake booster is an integral component in modern vehicles, providing the driver with the necessary assistance to bring a vehicle to a stop safely. The use of engine vacuum and a diaphragm allows for more efficient and effortless braking. By reducing the physical effort required and maintaining a consistent brake feel, brake boosters play a fundamental role in ensuring road safety.